Injury:年轻患者肱骨近端四部分骨折内固定治疗效果满意
2013-05-29 Injury 丁香园
肱骨近端四部分骨折是目前创伤骨科处理过程中的难点,常用的治疗方法有闭合复位石膏经皮克氏针固定,切开复位内固定或外固定,假体置换。因肱骨头软组织覆盖较少,内固定后容易出现肱骨头无菌性坏死,对老年人通常推荐进行肩关节置换。而对年轻人而言,因引发肱骨头四部分骨折的外因通常是极高的暴力,常常出现较为严重的骨折碎裂和关节脱位,并合并较为严重的软组织挫伤,内固定治疗更为困难,但因置换假体后期的无菌性松动,不稳
肱骨近端四部分骨折是目前创伤骨科处理过程中的难点,常用的治疗方法有闭合复位石膏经皮克氏针固定,切开复位内固定或外固定,假体置换。因肱骨头软组织覆盖较少,内固定后容易出现肱骨头无菌性坏死,对老年人通常推荐进行肩关节置换。而对年轻人而言,因引发肱骨头四部分骨折的外因通常是极高的暴力,常常出现较为严重的骨折碎裂和关节脱位,并合并较为严重的软组织挫伤,内固定治疗更为困难,但因置换假体后期的无菌性松动,不稳定和假体周围感染等导致的关节功能障碍问题不容忽视,目前大部分学者均同意年轻患者在治疗肱骨头四部分骨折时首选方案应当是切开复位内固术,若后期出现肱骨头无菌性坏死后再行二期假体置换术则能取得较好的治疗效果。为进一步证实年轻患者肱骨头四部分骨折应当首选内固定治疗的观点,来自埃及的学者就43例年轻患者肱骨头四部分骨折合并肩关节脱位的患者进行了内固定术后随访结果的总结,相关结论发表在近期出版的injury杂志上。
43例年轻患者来源于学者所在医院2004年-2010年间住院治疗的病例。其中男性32例,女性11例,平均年龄29.2岁(19-40岁),共21例患者为肩关节前脱位,22例患者为肩关节后脱位;13例患者为解剖颈骨折,30例为外科颈骨折,患者接受手术平均时间为伤后7天。
手术方法:全麻,仰卧位,略抬高患者头侧,患侧上肢消毒暴露,允许手术过程中自由运动。标准胸三角肌入路,在肱骨大结节脊上切断部分胸大肌止点,以利暴露和牵引。分离肩袖,将小结节肌肉群牵向内侧,大结节肌肉群前牵向外侧,常规复位技术进行骨折复位,外科颈可以将小结节的内侧脊或结节间沟作为复位标志点。头部解剖复位后临时固定,将大结节复位,并使用缝线缝合。14例患者仅靠克氏针即达到骨折牢靠固定,另29例患者使用肱骨近端钢板进行固定以确保骨折固定的牢靠性。平均手术时间2.5h,平均手术失血600ml。术后患肢悬吊,术后5天开始标准康复功能锻炼。克氏针固定患者术后2月取出固定针。
记录患者的肩关节Constant评分,并采用肱骨前后位和肩胛骨侧位片评估患者的骨折愈合和并发症情况。
研究结果如下:
4例患者失去随访,如表1所示,其余39位患者平均随访时间26月(18-35月)。在至少18个月的随访中,所有患者平均前侧抬高角度145度(90-170度),平均Constant评分77分(65-90)。9例患者出现轻度疼痛;3例患者出现中度疼痛。
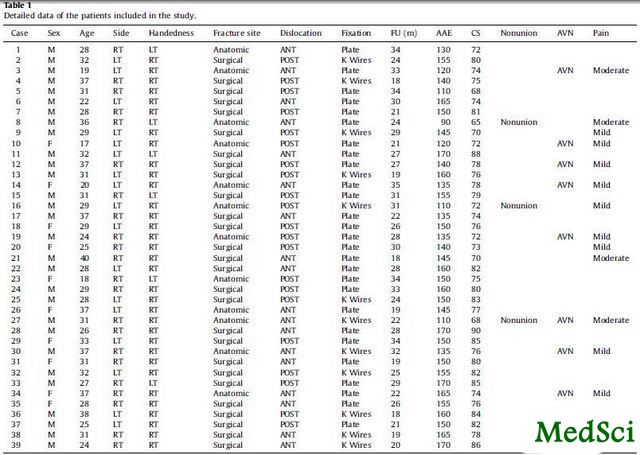
表1:纳入研究患者的相关统计学数据
将患者按照解剖颈及外科颈骨折进行分组(组1,解剖颈骨折,12例;组2,外科颈骨折,27例),外科颈骨折患者功能Constant评分要好于解剖颈组;但前脱位和后脱位组间比较无显著差异。
并发症:1例患者出现术中腋动脉分支断裂;1例患者术后5周出现螺钉退钉;3例患者出现骨折不愈合,均发生在组别1中;7例患者出现肱骨头无菌性坏死,其中组别1中6例,组别2中1例,5例患者无显著症状,2例患者因疼痛接受半肩置换;2例患者出现肩关节术后感染,行清创控制感染,1例患者,1例持续存在行钢板取出+后期半肩置换;1例患者术后出现骨折畸形愈合。
研究者总结:肱骨头四部分骨折的手术难点在于肩袖的功能特点要求骨折固定时需要达到解剖位置以保证肩关节的功能完好;在进行骨折解剖复位过程中应当尽可能的保证骨折碎块上软组织血供的完整性;骨折解剖复位进行内固定时要达到绝对的坚强固定以保证后期肩关节功能锻炼的进行。本试验研究发现骨折的部位是影响手术并发症和术后功能的一个重要因素,解剖颈骨折可能提示更差的功能预后;即使在良好的外科操作技术下,肱骨头的无菌性坏死仍是一个较难以避免的并发症,但因内固定创伤相对较小,术后并发症较少,术后康复功能锻炼更容易,即使出现无菌性坏死也不一定有临床症状,后期关节功能较差时再行二期关节置换后功能效果更好等原因,作者推荐对年轻患者的肱骨头四部分骨折首选切开复位+内固定治疗。
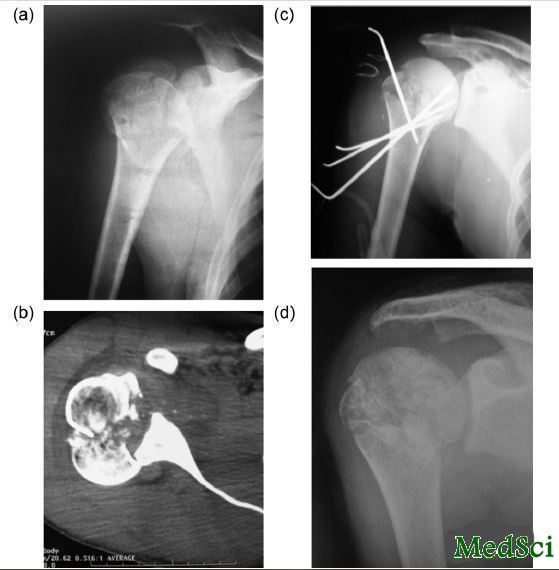
图1:病例17,37岁男性,肱骨头外科颈四部分骨折合并肩关节前脱位,钢板固定,术前前后位X片,术前CT片,术前CT三维重建片,术后前后位X片
图2:病例4,37岁男性,肱骨头外科颈四部分骨折合并肩关节后脱位,克氏针固定,术前前后位X片,术前CT片,术后前后位X片,术后12周随访时前后位X片

Four-part fracture dislocations of the proximal humerus in young adults: results of fixation.
INTRODUCTION
Four-part fracture dislocations of the proximal humerus occurring in young age are extremely difficult fractures with a high incidence of complications. The risk of avascular necrosis is high; hence, prosthetic replacement is the treatment of choice in older patients with these complex fractures; on the other hand, the longevity of the prosthesis is the main concern in young age. Thus, every effort should be made to fix these fractures in the young. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the results of fixation in a series of young patients with four-part fracture dislocations; to support the trend to fix these fractures; and reserve prosthetic replacement to older patients.
METHODS
In a prospective study, 39 patients younger than 40 years of age with four-part fracture dislocations were treated with open reduction and fixation either with K-wires or with a proximal humerus plate. Ethibond sutures were used in all patients to supplement fixation of tuberosities. In 18 patients, the dislocation was anterior and in 21 patients it was posterior. Twelve patients had an anatomic neck fracture and 27 had a surgical neck fracture. Surgery was performed within 1 week after the injury. Physiotherapy was initiated according to the general condition of the patient and the stability of fixation; the average time was 5 days after surgery.
RESULTS
Patients were followed up for an average of 26 months. Union was achieved in 36 patients and three patients had nonunion, all in anatomic neck fractures. Avascular necrosis developed in eight patients, seven of which were fractures of the anatomic neck and one was in the surgical neck. The average Constant score was 77; 26 patients were pain free, nine had mild pain and four had moderate pain. The mean active anterior elevation was 145°. Patients were divided into two groups based on the anatomic configuration of the fracture; in 12 patients (group 1), the head was fractured at the anatomical neck and in 27 patients (group 2), the head was fractured at the surgical neck. In group 2, the active anterior elevation was significantly better and the Constant score was higher.
CONCLUSIONS
Anatomical reduction and rigid fixation with meticulous surgical technique can lead to satisfactory results. The results in surgical neck fractures are superior to anatomic neck fractures with significantly less complications.
作者:Injury
版权声明:
本网站所有注明“来源:梅斯医学”或“来源:MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明“来源:梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,本网所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,转载内容不代表本站立场。不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言





#治疗效果#
54
#Injury#
79
#骨折内#
99
#肱骨#
76
#年轻患者#
85